MOMMY TALKS PODCAST Episode 13
- MOMMY TALKS PODCAST
Everyone has a different goal that they want to achieve concerning their family's financial freedom. But ultimately it all boils down to basically the same thing for everyone. We all want to provide our children the best life possible and enjoy every moment of living that life with them.
How does one do that?
Maybe you want to buy a new car. Or maybe you are contemplating making an even bigger purchase like buying a house for your family.
Will you be able to do so at affordable rates if you have a low credit score?
Probably not!
I mean sure, you may get approved, but at a much higher interest rate than someone with good or exceptional scores.
Your credit score can either be your biggest obstacle or your best asset in achieving your dreams. Providing a better life for your family can boil down to interest rates alone.

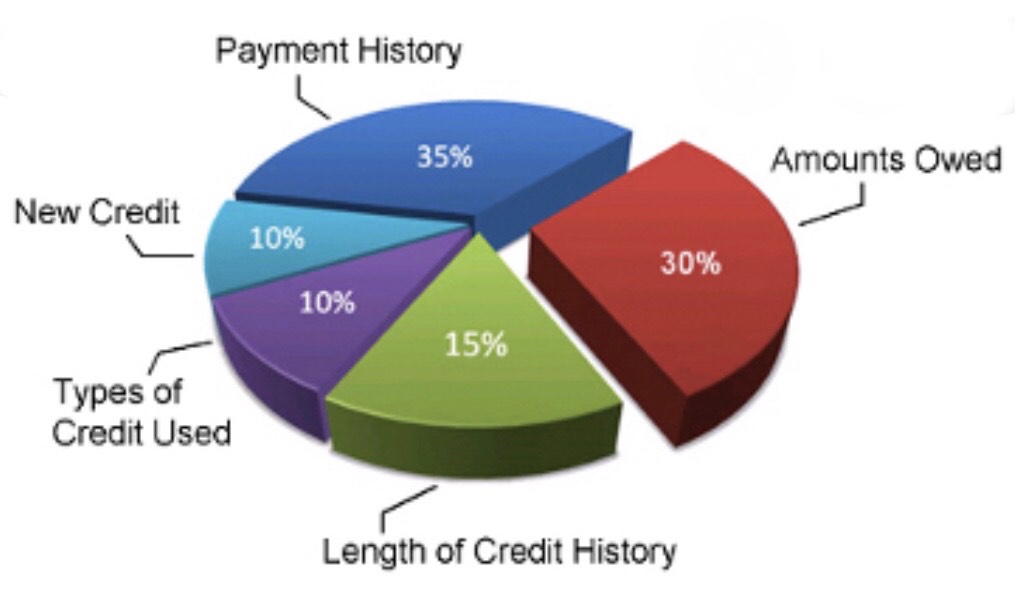
Five Factors That Make Up Your Credit Score

The key to improving your credit is first understanding how your credit score is calculated and the different factors that go into determining your score.
1. Payment History. Lenders are most concerned with whether or not you pay your bills. The best indicator of this is how you’ve paid your bills in the past. A payment isn’t considered late until 30 days past the due date. Once considered late, this payment can decrease your score.
If you have 30 or 60 day late payments that are an infrequent occurrence, they shouldn't cause lasting damage to your credit score. Unless they are within the last two years or so, or occur on a regular basis. In this case, the fact that you are habitually late with your payments can cause long-term damage to your credit scores.
Once you have a 90 day late payment reflected on your credit, even just once, your credit score will be damaged up to seven years. From a scoring perspective, a single 90 day late payment is as damaging to your credit score as a bankruptcy filing, tax lien, collection, judgment, even a repossession.
The importance of payment history accounts for 35% of your credit score. Even one missed payment can have a negative impact on your score. The more consistently and timely you make your payments, the higher your credit score will be.
2. Level of Debt. The amount of debt you have in comparison to your credit limit is known as credit utilization. The higher your credit utilization—the closer you are to your limits—the lower your credit score will be. This factor accounts for 30% of your credit score. As long as you’re not being charged to keep an unused account, it’s best practice to keep it active. It can help decrease your overall utilization ratio and maybe even your length of credit history. We'll get to that in the next section.
Surprisingly 1% - 9% is the ideal credit utilization. Using this amount of your credit is the fastest way to help improve your score, assuming that you make all your payments on time and are otherwise responsible. This is contrary to the popular belief that one should keep their credit utilization at 30%. In fact, the more accounts you have with credit utilization at 30% or higher, the worse it is for your credit score.
3. Length of Credit History. The credit scoring algorithms calculate the average of all the accounts you have open. This average age of accounts is your “credit age” also known as the length of credit history. This factor accounts for 15% of your credit score. One term to be aware of is the Average Age of Accounts (AAoA). This is the formula FICO® uses to calculate your average length of credit history. It is broken down into three parts:
- How long accounts have been open
- How long specific types of accounts have been open (revolving and installment)
- How long it’s been since you last used these accounts
It’s a simple calculation: divide the ages of your oldest and newest accounts by your total number of accounts.
Having an “average age” of 7 years or more is favorable because it gives more information about your spending habits. It’s good practice to leave open the positive accounts that you’ve had the longest, for as long as possible. The truth is that credit affects your life as soon as you become an adult and continues to do so for your whole life.
That's why 18, or younger, is a good age to start building credit. This can be done primarily from the assistance of the child’s parents. As long as the parents have good credit or are working on rebuilding their credit they can add their child to accounts as an authorized user. Most cards allow authorized users younger than 18. Some have age minimums, while others don't.
When you become an authorized user, you’re added to someone’s credit card account. This can help you get approved for your own account because as long as the credit card company reports authorized users to the credit bureaus their credit history will reflect as yours. Be sure to ask someone you trust, like a family member or close friend, and make sure they have good credit.
Now, what happens when someone removes you as an authorized user? Usually, the card issuer will stop reporting the account on the authorized user’s credit report. Some lenders will entirely remove the account’s history from the authorized user’s credit report. This can help or hurt the person’s credit score.
If the primary account holder’s account is in good standing, it will be bad for the authorized user’s score. They were receiving the benefit of that person’s payment history on the account, low credit utilization, and the length of time they’ve had the card and stand to lose it all if and when they are removed. This is why, while it can be beneficial to be added to someone’s account as an authorized user it is more important to work on building your own great score, rather than depend on someone else’s.
This factor constitutes 10% of your credit score. Each time you submit an application that requires a credit check, an inquiry is placed on your credit report showing that you have made a credit-based application. Too many inquiries in a short time could make it look like you are seeking loans and credit cards that you may not be able to pay back. It is therefore advisable to keep your inquiries at a minimum to preserve your credit score.
5. Credit Mix. Having different kinds of accounts is favorable because it shows that you have experience managing a mix of credit. This isn’t a significant factor in your credit score unless you don’t have much other information on which to base your score. Open new accounts as you need them, not to simply have what seems like a better mix of credit.
This accounts for 10% of your credit score. It is better to have a diverse portfolio of credit including car loan, credit card, student loan, mortgage, or other credit products. This is an indication that you have experience in managing different lines of credit.

Factors That Do Not Matter In Determining Your Credit Score